
Photovoltaic or solar panels are a great way to generate electricity. But how do these cells work and what is the cost? In this article, we'll break down what they are, how they are manufactured, and how they work to make electricity.
Solar panels
A solar panel is made from solar cells, which convert light into electricity directly. This is called the photovoltaic process and it is both a physical process and a chemical one. This technology is becoming increasingly popular in commercial and residential settings. It can be used to produce electricity using renewable energy sources.
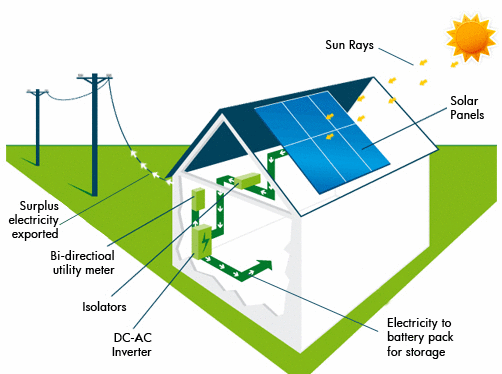
The panels are made of several photovoltaic cells, which are small pieces of silicon sandwiched together. These cells are exposed to sunlight, which knocks out electrons and causes them to flow towards a conductive plate. The electricity created is then passed through wires and to an inverter. The inverter turns the direct current and alternating current into electricity that can be used to power homes or buildings.
Photovoltaic cell
Photovoltaic cells are used to convert light energy into electricity. They absorb light and convert it to positively charged particles, known as electrons. The electrons can flow through the material as an electric current. This electrical current can be extracted using conductive metal contacts such as grid-like lines that are found on solar cells' surfaces. These solar cells produce electricity that can be used to power homes and the electric grid.

Photovoltaic cells in solar panels use the phenomenon of the photovoltaic effect to convert light into electricity. The photons emitted from sunlight knock electrons out of silicon atoms in solar cells. These electrons circulate freely within the cells and convert sunlight into electricity.
Manufacturing process
The manufacturing process for solar panels includes a series of steps. The solar cells are first laminated to stop water and shock entering the panel. Next, the solar cells are placed in an aluminum frame with a tedlar or mylar backsheet and a glass or plastic cover. The panels are then checked for quality throughout manufacturing.
The solar cells then get soldered together. They are then subject to further quality control and are sorted according their power output. Next, they are connected to metal connectors. These solar cells can then be assembled into PV modules. The cells are connected together in series, with the positive contact on one cell and the negative contact on another. Solar cells come in a standard size. 60 cells is the minimum size for residential or commercial projects.
Prices
The cost of solar cells and photovoltaic panels depends on many factors. These factors include the amount and quality of sunlight received by the household. For instance, a home with primarily gas appliances will use less electricity than one with mostly electric appliances. Another factor that impacts the cost of a panel is its efficiency. The more efficient the panels are, the more money you'll save. You should also consider the amount of roof space your home has.
Solar panels typically cost $0.30 per watt. The more solar panels you have, the more expensive they will be. A 1,500-square-foot home will require 16 panels to produce enough electricity to power its electric use. Additional panels might be required if the home is situated in an area with shaded or east facing areas.
Efficiency
The efficiency of solar panel is an indicator of how efficient they convert sunlight into electricity. A solar panel that is 100 percent efficient would convert all sunlight it receives into electricity. According to scientists solar efficiency refers to the ratio of solar energy produced to solar energy consumed.
The efficiency level of solar panels will vary depending on many factors. Some cells, for example, may only capture a fraction or all of the sunlight. Because sunlight comes in a variety of wavelengths, semiconductors cannot capture all of this light. Some light can also be absorbed or reflected by semiconductors. These inefficiencies can reduce the efficiency and effectiveness of solar panels as well as the systems that make them up.